P waves travel faster than S waves, and are the first waves recorded by a seismograph in the event of a disturbance P waves travel at speeds between 1 and 14 km per second, while S waves travel significantly slower, between 1 and 8 km per second The S waves are the second wave to reach a seismic station measuring a disturbanceWaves are one of the ways in which energy may be transferred between stores Waves can be described as oscillations, or vibrations about a rest position*/ Light waves across the electromagnetic spectrum behave in similar ways When a light wave encounters an object, they are either transmitted, reflected, absorbed, refracted, polarized, diffracted, or scattered depending on the composition of the object and the wavelength of the light
Seismic Waves Science Learning Hub
S waves meaning in science
S waves meaning in science-A wave is a transfer of energy, usually through a form of matter called a medium For example, the energy provided by the kids at play travels through the medium of the parachute There are alsoThe types of waves most commonly studied in classical physics are mechanical and electromagneticIn a mechanical wave, stress and strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium A mechanical wave is a local deformation (strain) in some physical medium that propagates from particle to particle by creating local stresses that cause strain in neighboring particles too



Wave Types Of Waves Properties Of Waves Application Of Waves Byju S
A wave is a disturbance in a medium that carries energy without a net movement of particles It may take the form of elastic deformation, a variation of pressure, electric or magnetic intensity, electric potential, or temperatureExamples of transverse waves include ripples on the water surface, vibrations on a guitar string, and seismic Swave Electromagnetic waves have transverse characteristics, but unlike other mechanical waves, they can propagate in a vacuumSecondary waves, or Swaves, are seismic waves produced by an earthquake As one side of a fault slips past the other, the pressure that had been stored is released and travels radially away from
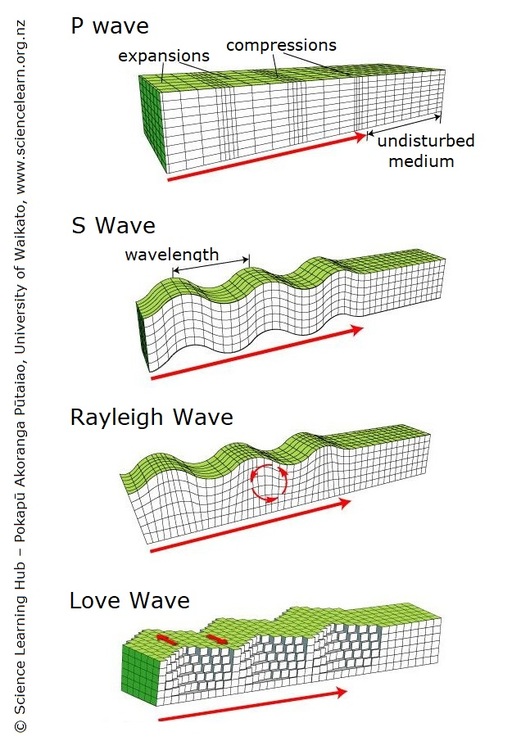
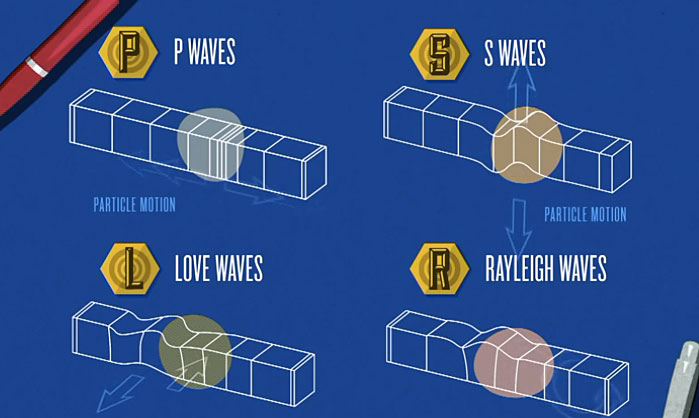
There are two types of seismic wave, namely, 'body wave' and 'surface wave' There are two kinds of body waves primary (Pwaves) and secondary (Swaves) Surface waves are analogous to water wavesS waves are transverse waves S waves travel in a motion similar to a rope held tight at one end while the other end is lifted rapidly back and forth S waves only travel through solids and do not travel through the liquid outer core of the EarthS Waves The second type of body wave is the S waveor secondary wave, which is the second wave you feel in an earthquake An S wave is slower than a P wave and can only move through solid rock, not through any liquid medium It is this property of S waves that led seismologists to conclude that the Earth's outer coreis a liquid
The definition of wave is to move back and forth in a swinging motion, or to style your hair inA wave is a disturbance in a medium that carries energy without a net movement of particles It may take the form of elastic deformation, a variation of pressure, electric or magnetic intensity, electric potential, or temperatureS waves and P waves are the two types of seismic waves produced by all earthquakes P waves are primary waves because they arrive at seismic reporting stations first These shear waves are secondary waves because they travel at slightly slower speeds and are the second set of seismic waves recorded on seismographs



Wave Propagation



Prentice Hall Earth Science Ch08 Earthquakes Layers Of Earth
There are two types of seismic wave, namely, 'body wave' and 'surface wave' There are two kinds of body waves primary (Pwaves) and secondary (Swaves) Surface waves are analogous to water wavesTransverse waves can be represented by a sine or cosine function, called a wave function The wave function determines the displacement of a particle from the axis of propagation at different times and distances from the origin This displacement is proportional to the sine or cosine of the angle that the displacement vector makes with the axisPrimary waves are made up of compression waves, also known as pushpull waves The individual waves, therefore, push against one another, causing a constant parallel, straight motion S waves are transverse waves, which means they vibrate up and down, perpendicular to the motion of the wave as they travel


Seismic Wave Msrblog



Learn About Earthquake Waves Chegg Com
If there aren't any S waves marked on your seismogram, it probably means the earthquake happened on the other side of the planet S waves can't travel through the liquid layers of the earth so these waves never made it to your seismograph The surface waves (Love and Rayleigh waves) are the other, often larger, waves marked on the seismogramWaves are one of the ways in which energy may be transferred between stores Waves can be described as oscillations, or vibrations about a rest positionSeismic waves are energy waves that are generated by an earthquake or explosion and propagate within the Earth or on its surface Earthquakes occur when there is a movement of Earth's tectonic plates



Earthquake Glossary


What Are Seismic Waves Kqed
The last one is tiny, so the biggest wave in the group is in the middle, and if there are 14 waves in a group, the seventh wave is the biggest Gnarly The Surprisingly Strange Physics of WaterHowever, they may propagate in liquids with high viscosityNoun Geology a transverse earthquake wave that travels through the interior of the earth and is usually the second conspicuous wave to reach a seismograph


What Is Seismology And What Are Seismic Waves


What Is Seismology And What Are Seismic Waves
A wave is a disturbance in a medium that carries energy without a net movement of particles It may take the form of elastic deformation, a variation of pressure, electric or magnetic intensity, electric potential, or temperatureThe last one is tiny, so the biggest wave in the group is in the middle, and if there are 14 waves in a group, the seventh wave is the biggest Gnarly The Surprisingly Strange Physics of WaterIn science, work is defined as the movement of an object in the direction of the force applied to it Waves do work when they move objects We can see this work when heavy logs move across ocean basins or sand is transported Work can also be converted into sound energy heard when waves crash on the shore



P Wave The Difference Between P And S Waves And P Wave Formula



S Waves Are Seismic Waves
P (Primary) and S (Secondary) Waves are Body Waves often associated with Seismic Waves as in Earthquakes Both Body Waves and Surfaces waves comprise an earthquake, but the body waves arrive firstS Rajasekaran, in Structural Dynamics of Earthquake Engineering, 09 1622 Mantle The volume of the mantle is % Velocities of P wave and S wave are 81 and 45 km/s respectivelyPeridotite is the rock type found in mantle From 50 to 250 km seismic wave velocity decreases, indicating a change in compositionHere P wave velocity decreases from 81 to 78 km/s and S wave velocityS waves are transverse waves S waves travel in a motion similar to a rope held tight at one end while the other end is lifted rapidly back and forth S waves only travel through solids and do not travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth



Seismic Waves Physical Geography


Seismic Wave Msrblog
Seismic waves are energy waves that are generated by an earthquake or explosion and propagate within the Earth or on its surface Earthquakes occur when there is a movement of Earth's tectonic platesIf there aren't any S waves marked on your seismogram, it probably means the earthquake happened on the other side of the planet S waves can't travel through the liquid layers of the earth so these waves never made it to your seismograph The surface waves (Love and Rayleigh waves) are the other, often larger, waves marked on the seismogramS waves, also called shear or transverse waves, cause points of solid media to move back and forth perpendicular to the direction of propagation;



Seismic Wave An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Seismic Shadow Zones Introduction To P S Wave Shadow Zones Educational Youtube
A gravitational wave is an invisible (yet incredibly fast) ripple in space We've known about gravitational waves for a long time More than 100 years ago, a great scientist named Albert Einstein came up with many ideas about gravity and space Albert Einstein, official 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics photographThere are two types of seismic wave, namely, 'body wave' and 'surface wave' There are two kinds of body waves primary (Pwaves) and secondary (Swaves) Surface waves are analogous to water wavesSwave (secondary wave, shear wave, transverse wave) An elastic body wave in which particles oscillate about a fixed point but in a direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave energy Swaves cannot travel through a fluid, since a fluid cannot support shear


Surface Waves Seismic Resilience



Wave Types Of Waves Properties Of Waves Application Of Waves Byju S
S waves and P waves are the two types of seismic waves produced by all earthquakes P waves are primary waves because they arrive at seismic reporting stations first These shear waves are secondary waves because they travel at slightly slower speeds and are the second set of seismic waves recorded on seismographsSurface waves Surface waves are typically generated when the source of the earthquake is close to the Earth's surface As their name suggests, surface waves travel just below the surface of the ground Although they move even more slowly than Swaves, they can be much larger in amplitude and are often the most destructive type of seismic waveElectromagnetic wave definition is one of the waves that are propagated by simultaneous periodic variations of electric and magnetic field intensity and that include radio waves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, Xrays, and gamma rays



Section 9 2 Define Seismic Waves And Focus Ppt Video Online Download



What Is Seismic Wave What Does Seismic Wave Mean Seismic Wave Meaning Explanation Youtube
A standing wave can only be formed when a wave's motion is restricted within a given, finite space In more specific terms, a standing wave is a wave that oscillates in time, but its peak amplitude profile does not move in space Also known as a stationary wave, a standing wave is formed due to interferenceAn S wave, or shear wave, is a seismic body wave that shakes the ground back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is movingS wave definition is a wave (as from an earthquake) in which the propagated disturbance is a shear in an elastic medium (such as the earth)
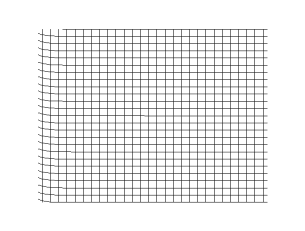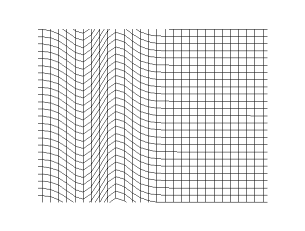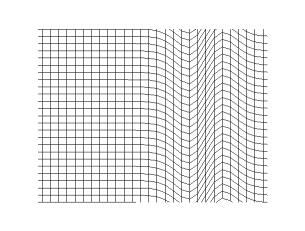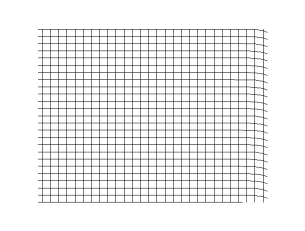


S Wave Wikipedia



S Waves Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
See Article History Transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave's advance Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic (eg, radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves Read More on This TopicEspecially the return of light or sound waves from a surface How to use reflection in a sentenceSwaves are transverse waves, meaning that the oscillations of an Swave's particles are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, and the main restoring force comes from shear stress Therefore, Swaves can't propagate in liquids with zero (or very low) viscosity;



Seismic Waves Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation



Seismic Waves
Information and translations of Swave in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the webWhat does wave mean?Definition of Swave in the Definitionsnet dictionary Meaning of Swave What does Swave mean?



S Wave Wikipedia


Good Vibrations What Earthquakes Can Tell Us About The Earth Science Over Everything
The Cassini spacecraft captured this image of Saturn's aurora using infrared waves The aurora is shown in blue, and the underlying clouds are shown in red These aurorae are unique because they can cover the entire pole, whereas aurorae around Earth and Jupiter are typically confined by magnetic fields to rings surrounding the magnetic polesAs the wave passes, the medium is sheared first in one direction and then in anotherS waves also called secondary waves and shear waves, are the second waves to hit the seismographs They are transverse waves, which means that the motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation



Seismic Wave Wikipedia



Seismic Waves Science Learning Hub
Swave (secondary wave, shear wave, transverse wave) An elastic body wave in which particles oscillate about a fixed point but in a direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave energy Swaves cannot travel through a fluid, since a fluid cannot support shearWhen an earthquake occurs, the shockwaves of released energy that shake the Earth and temporarily turn soft deposits, such as clay, into jelly (liquefaction) are called seismic waves, from the Greek 'seismos' meaning 'earthquake' Seismic waves are usually generated by movements of the Earth's tectonic plates but may also be caused by explosions, volcanoes and landslidesPrimary waves are made up of compression waves, also known as pushpull waves The individual waves, therefore, push against one another, causing a constant parallel, straight motion S waves are transverse waves, which means they vibrate up and down, perpendicular to the motion of the wave as they travel



Seismic Waves Physical Geography


Surface Waves Seismic Resilience
Ocean waves are carried by water, sound waves are carried by air, and the seismic waves of an earthquake are carried by rock and soil A wave is a disturbance travelling through matter or space, transferring energy from one place to anotherP waves are like the lightning, and S waves are like the thunder The P waves travel faster and shake the ground where you are first Then the S waves follow and shake the ground also If you are close to the earthquake, the P and S wave will come one right after the other, but if you are far away, there will be more time between the twoReflection definition is an instance of reflecting;



Surface Wave Wikipedia


Body Waves Seismic Resilience
Define secondary wave secondary wave synonyms, secondary wave pronunciation, secondary wave translation, English dictionary definition of secondary wave An earthquake wave in which rock particles vibrate at right angles to the direction of wave travel
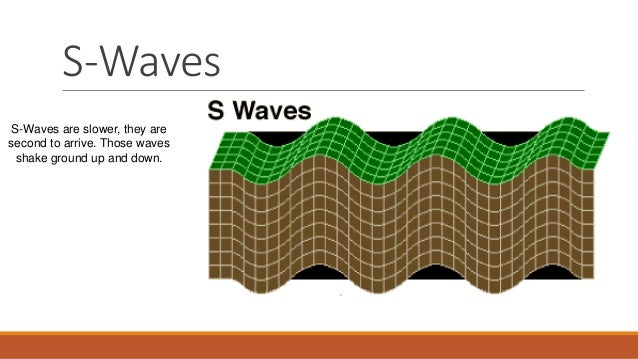


Seismic Waves



Seismic Waves Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation



Compare Contrast Connect Seismic Waves And Determining Earth S Structure Manoa Hawaii Edu Exploringourfluidearth



The Science Of Earthquakes
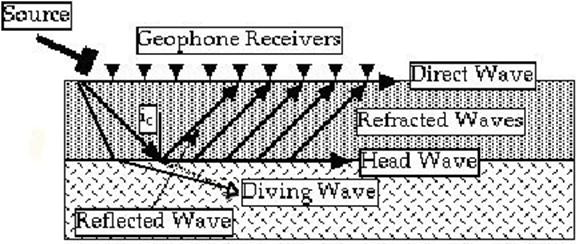


Earthquake Seismology I


Earth Structure Earth Science Visionlearning



P And S Waves Meghan Environmental Science



Evidence For Earth S Layers 8th Grade Science



Wave Water Britannica
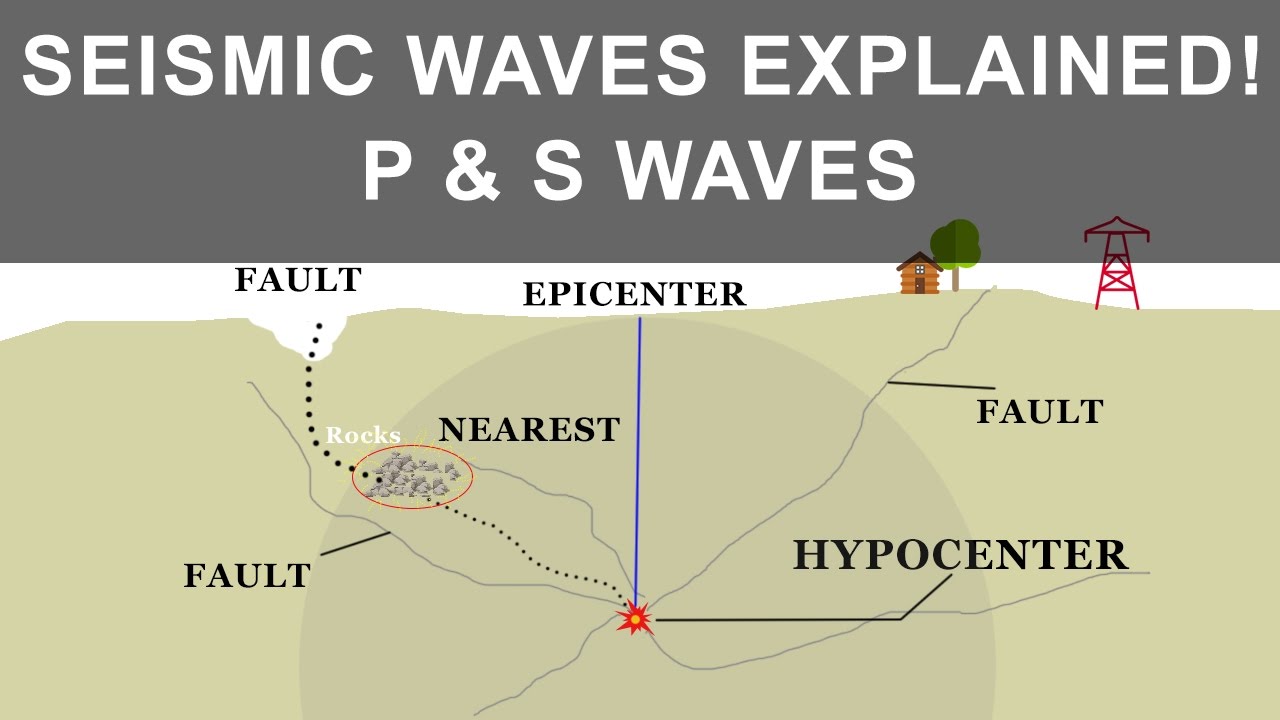


How Earthquake Occurs And What Causes It Seismic Waves P And S Waves Youtube
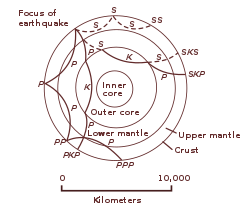


Seismic Wave Wikipedia



Seismic Survey Description Methods Facts Britannica



Seismic Waves P S And Surface Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology


How Do I Read A Seismogram



Earthquake Glossary


Good Vibrations What Earthquakes Can Tell Us About The Earth Science Over Everything



What Are Surface Waves Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
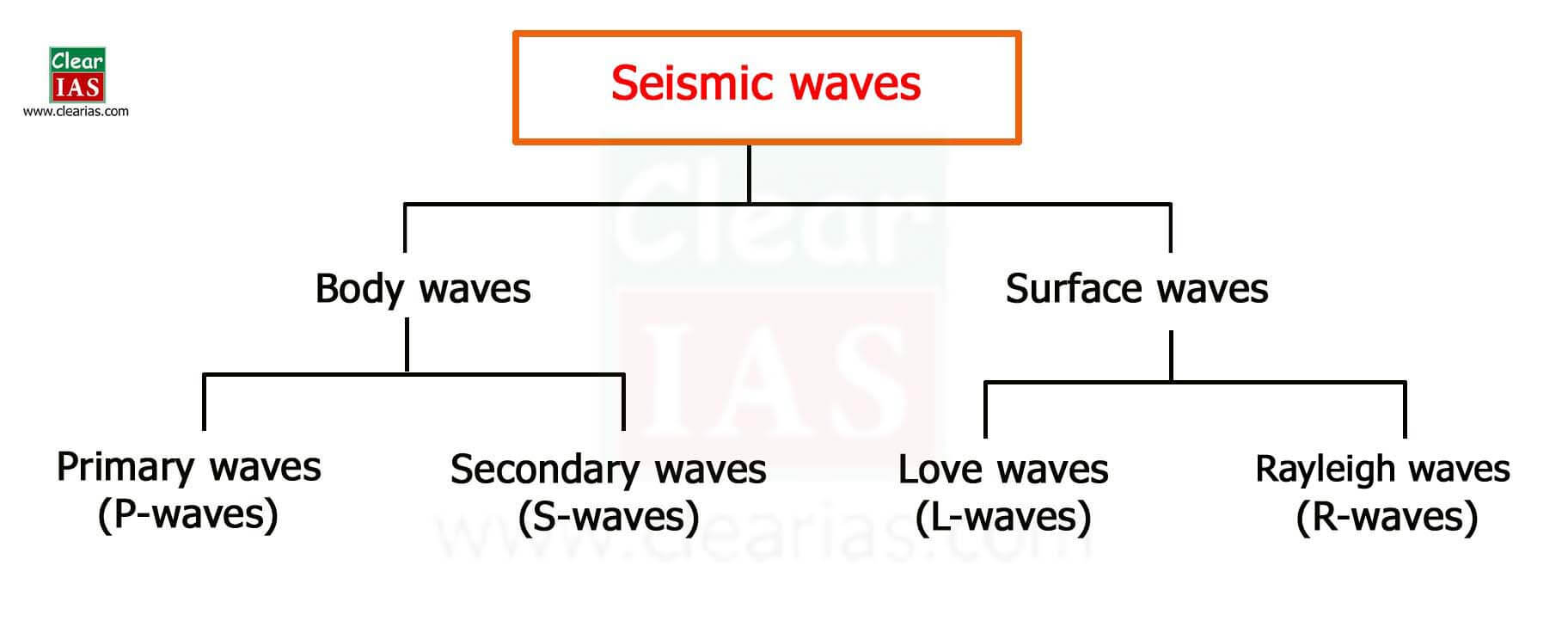


Earthquakes Everything You Need To Know Clearias



Seismograph Applications Of The Seismograph Britannica



Primary Wave Seismology Britannica



P Wave An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Seimic Waves And Earth S Interior


Types Of Earthquake Waves



Seismic Waves Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation


Physics Tutorial Categories Of Waves
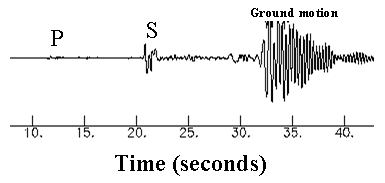


Science For Kids Earthquakes



Compare Contrast Connect Seismic Waves And Determining Earth S Structure Manoa Hawaii Edu Exploringourfluidearth



Seismic Wave Britannica



Seismic Waves P S And Surface Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology


Seismic Waves Research And Analysis Intechopen



Earthquake Glossary
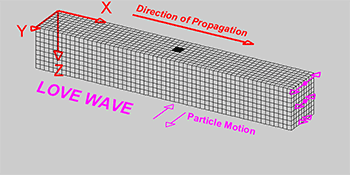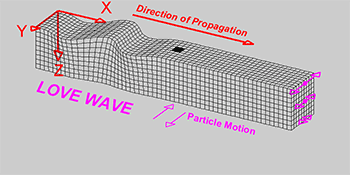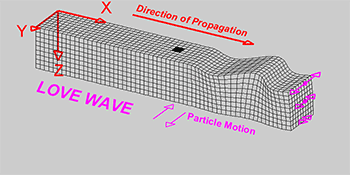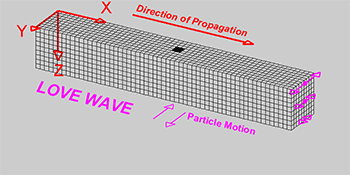


Explainer Seismic Waves Come In Different Flavors Science News For Students



Seismic Waves



S Wave Wikipedia



Seismic Waves Seismic Wave Earthquake Waves Seismic



Earthquakes And The Earth S Internal Structure Amnh



Seismic Wave Wikipedia



Seismic Waves Kaiserscience
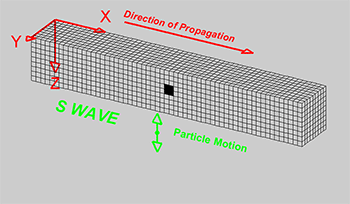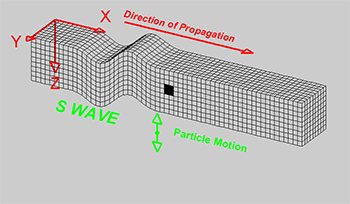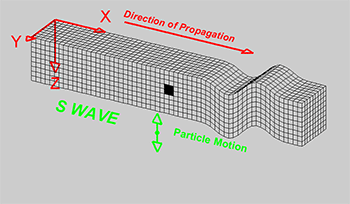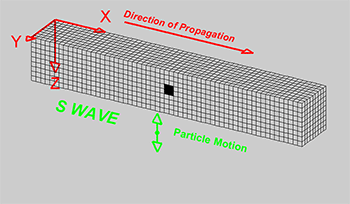


Explainer Seismic Waves Come In Different Flavors Science News For Students



What Are Surface Waves Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Explainer Seismic Waves Come In Different Flavors Science News For Students
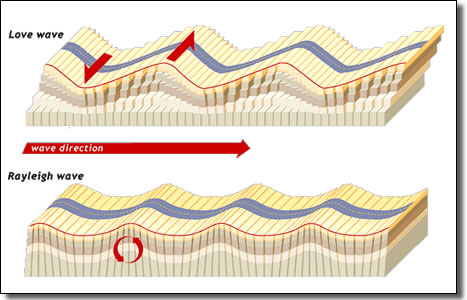


Earthquake Seismic Waves As Body Waves And Surface Waves


9 1 Understanding Earth Through Seismology Physical Geology
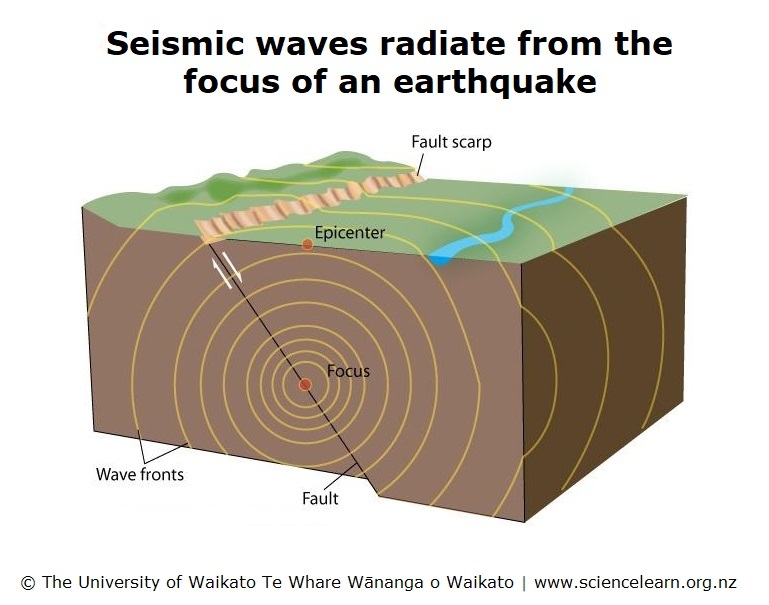


Seismic Waves Science Learning Hub



Seismic Waves And The Layers Of The Earth


Love Wave Wikipedia


Earthquakes And Seismology



Seismic Waves Video Khan Academy



Seismograph Applications Of The Seismograph Britannica



Seismic Wave Assignment Point



Seismic Waves Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation


Types Of Earthquake Waves


What Are Seismic Waves Kqed



Mechanical Wave Ck 12 Foundation
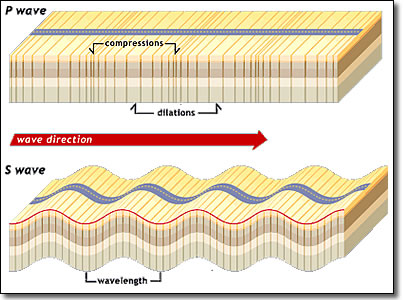


Earthquake Seismic Waves As Body Waves And Surface Waves



Secondary Wave Seismology Britannica



Earthquake Glossary



Seismic Wave Britannica
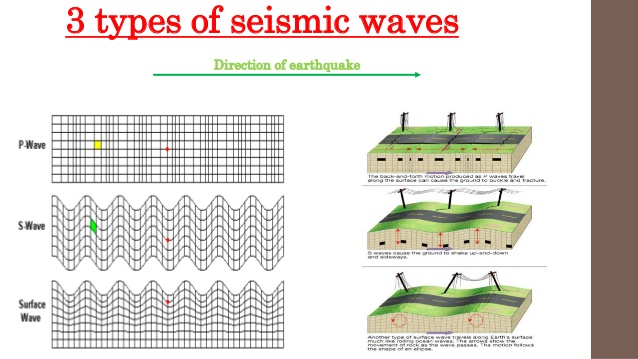


What Are The 3 Main Types Of Seismic Waves How Do They Differ From Each Other Socratic



Why S Waves Only Travel In Solids Video Khan Academy
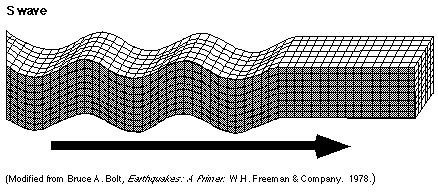


Seismic Waves



Seismic Shadow Zone Definition Overview Study Com


The Main Types Of Seismic Waves P S And Surface Waves
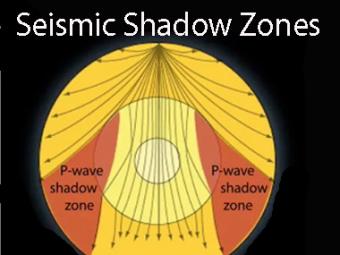


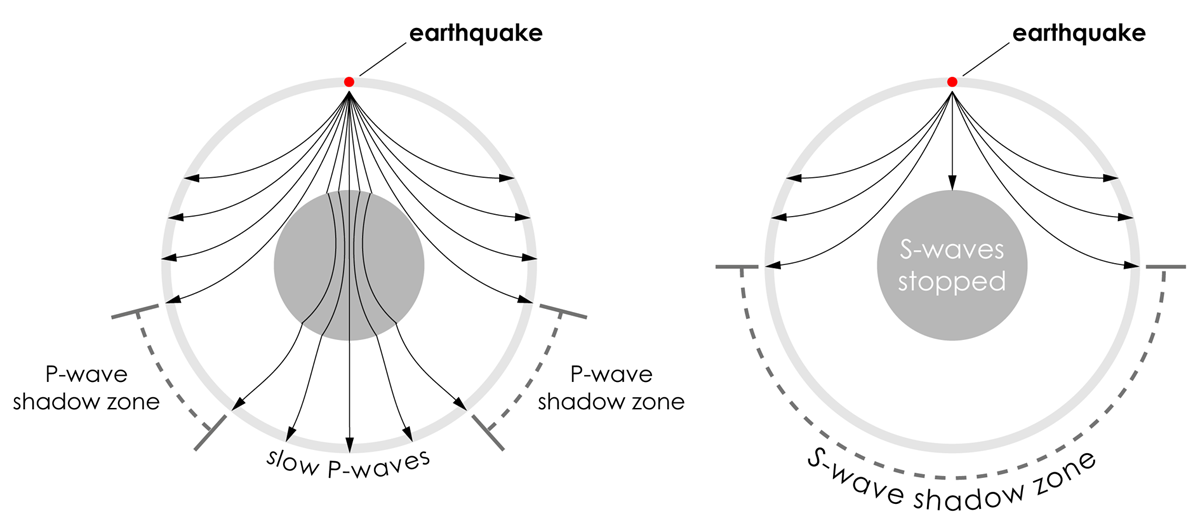
Seismic Shadow Zone Basic Introduction Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology



Seismic Waves Seismic Wave Earth Science Learning Science



Earthquake Glossary


Anatomy Of An Earthquake Exploring Earthquakes
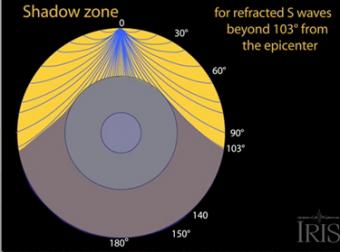


Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
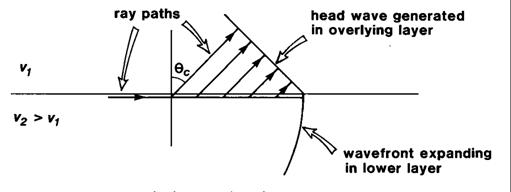


Earthquake Seismology I


Body Waves Seismic Resilience



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿